ABCC4、FCGR2A及BLK基因多态性与华南地区儿童川崎病遗传易感相关性研究
2017年5月
中华检验医学杂志,第40卷第5期 第372页-第377页
张媛,张白杜,刘云锋,皮蕾,车迪,张丽,顾晓琼
川崎病又称皮肤黏膜淋巴结综合征,是一种急性、自限性、病因不明的血管炎症性疾病,好发于5岁以下儿童。该病主要累及中小动脉,尤其是冠状动脉。部分患儿可发展成冠状动脉瘤、冠状动脉狭窄或血栓,甚至导致心肌梗死[1]。目前,该病已成为儿童后天性心脏病最常见原因之一。国外多项全基因组关联分析(genome-wide association study,GWAS)对日本、欧洲、韩国以及中国台湾人群的研究表明,Fcγ受体Ⅱa基因(Fc fragment of IgG receptor 2A, FCGR2A)、B淋巴细胞激酶(B lymphocyte kinase, BLK)和多药耐药蛋白(ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 4, ABCC4)基因区域的多个单核苷酸多态性(single nucleotide polymorphism,SNP)位点与川崎病易感密切相关,但在中国汉族人群特别是华南地区儿童患者中仍缺乏相关研究[2,3,4]。鉴于此,本研究采用时间飞行质谱生物芯片系统(Sequenom MassArray)进行基因分型,以探讨FCGR2A(rs1801274)、BLK(rs2254546)以及ABCC4(rs7320375、rs7329490、rs7986087)基因多态性位点是否与川崎病遗传易感性相关。
选取2013年10月至2015年11月于广州妇女儿童医疗中心就诊的华南地区92例川崎病儿童,男女比例为1.7∶1,平均年龄29.93个月。所有患儿均符合2004年美国心脏病协会的川崎病诊断标准[5],并依据不同冠状动脉损伤程度分为:冠状动脉正常或增粗、冠状动脉扩张和冠状动脉瘤3组。分类标准如下:冠状动脉扩张指冠状动脉5岁以内>3 mm,5岁以上>4 mm,或扩大的冠状动脉直径大于其近或远端血管直径的1.5倍;冠状动脉瘤指左冠状动脉或右冠状动脉主干内径和主动脉根部内径之比>0.3。冠状动脉内径4~7 mm,冠状动脉相应部位出现球形、囊性或梭形扩张,或呈串珠样改变,提示冠状动脉瘤;若冠状动脉明显扩张,冠状动脉内径>8 mm,则为巨大冠状动脉瘤。选取同期在广州妇女儿童医疗中心保健科体检的健康儿童194名作为健康对照组,男女比例1.5∶1,平均年龄为28.33个月。排除既往川崎病病史、感染性疾病、心血管疾病以及自身免疫性疾病。本研究得到了广州市妇女儿童医疗中心伦理委员会批准,所有对象均签署了知情同意书。
全血基因组DNA快速提取试剂盒购自北京亚能生物技术有限公司,DNA标本基因分型采用美国高科技生命科技公司的Sequenom MassArray系统。
抽取待检者静脉血2 ml,EDTA抗凝,采用全血基因组DNA快速提取试剂盒,严格按产品操作说明提取DNA。超微量紫外/可见光分光亮度计(Nanodrop2000)测量DNA样本浓度(>20 ng/μl)和纯度(A260/280=1.7~1.9),琼脂糖电泳显示大于10 000 bp的明亮单一条带,表明无DNA、蛋白污染,为合格DNA标本。将DNA标本置于-80 ℃冰箱保存备用。
每份DNA标本分型所需的量为10~20 ng。位点特异性多重PCR扩增以及延伸引物均使用MassArray Assay Designer3.1软件进行引物设计,并由北京华诺时代科技有限公司合成,见

基因分型结果应用PLINK1.9(http://pngu.mgh.harvard.edu/~purcell/plink/)软件进行分析。根据Hardy-Wemberg平衡定律检验所有SNP位点在人群中分布情况,以Person χ2检验及Fisher精确概率法对符合Hardy-Wemberg平衡定律的SNP位点的基因型和等位基因频率在川崎病组与正常对照组、冠状动脉正常及增粗、冠状动脉扩张组与冠状动脉瘤组间差异进行分析,计算χ2值、优势比(odds ratio,OR)、双侧95%CI和P值,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
所有SNP位点(rs1801274、rs2254546、rs7320375、rs7329490与rs7986087)均符合Hardy-Wemberg平衡定律(χ2=0.236,P=0.628;χ2=3.681,P=0.055;χ2=0.104,P=0.747;χ2=0.104,P=0.747和χ2=2.597,P=0.107),提示所选人群具有较好代表性。
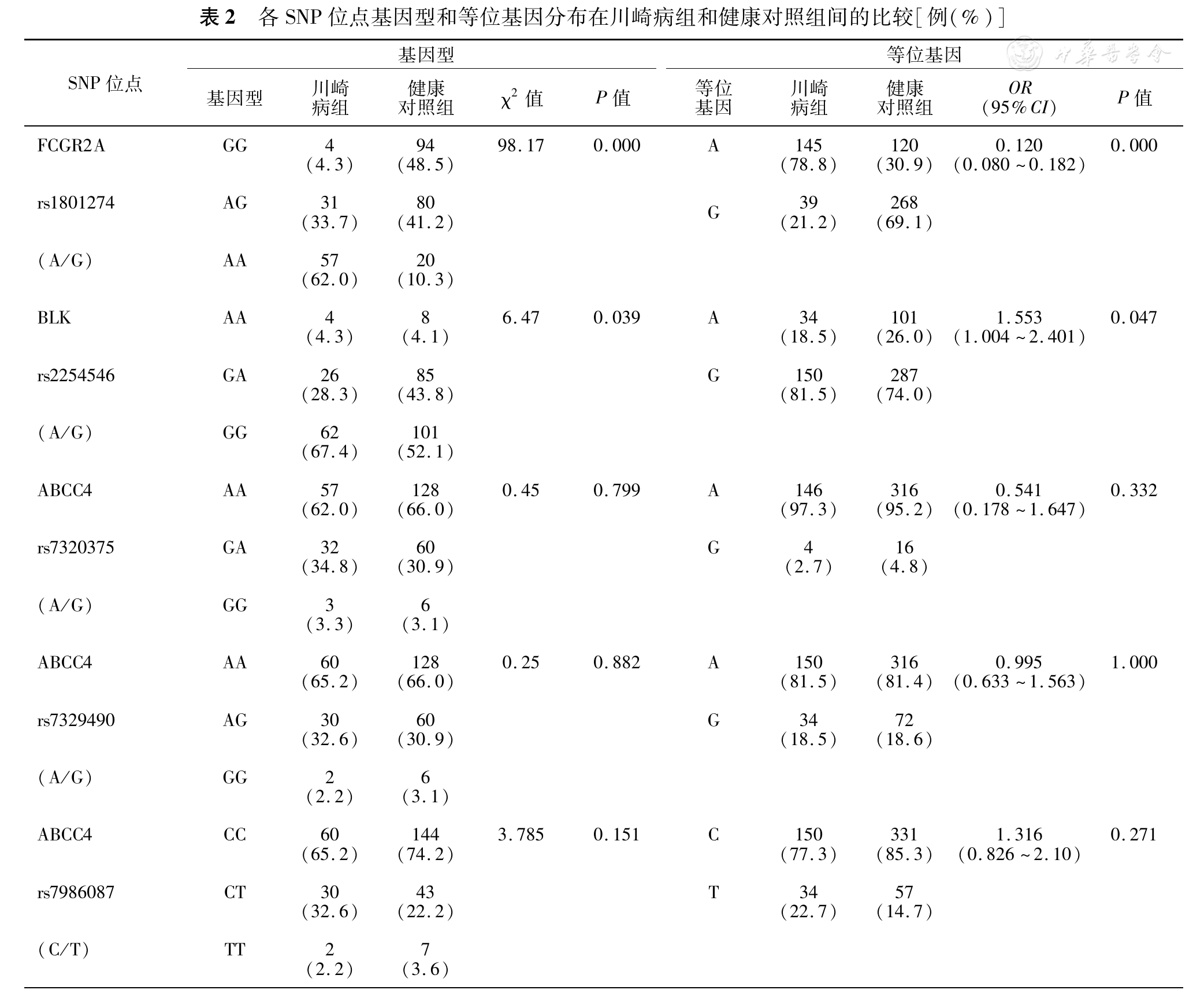
经Pearson χ2检验后,FCGR2A基因rs1801274位点的基因型分布和等位基因频率在川崎病组和健康对照组之间差异均有统计学意义(χ2=98.17,P=0.000;χ2=0.120,P=0.000),OR<1,A为风险基因。同样,BLK基因的rs2254546位点的基因型分布和等位基因频率在川崎病组和健康对照组之间差异也均有统计学意义(χ2=6.47,P=0.039;χ2=1.553,P=0.047),OR>1,G为风险基因。而ABCC4基因区域的rs7320375、rs7329490与rs7986087各SNP位点基因型和等位基因频率在两组间分布经Fisher精确概率法校正后差异无统计学意义(P均>0.05),见
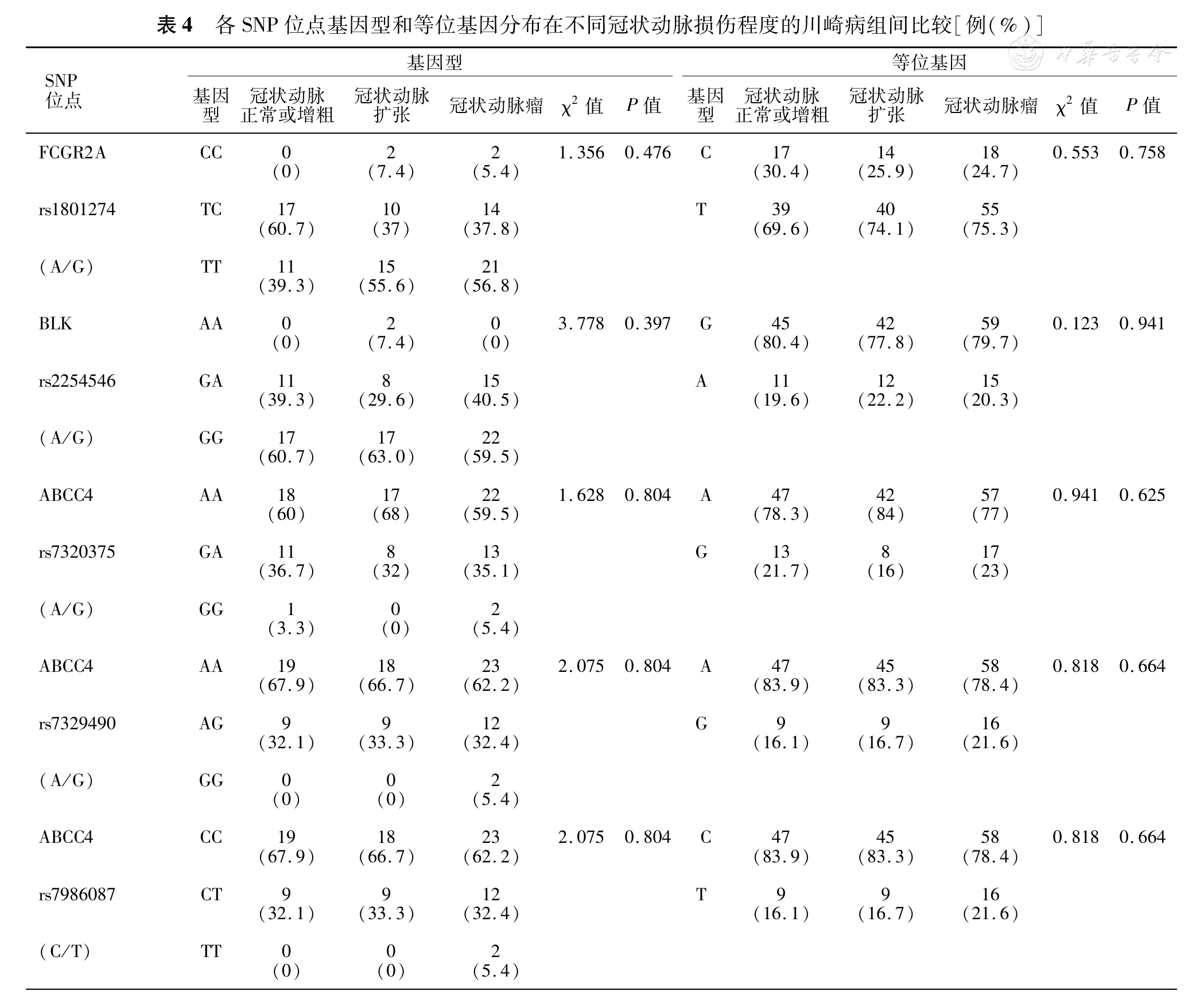
经Fisher精确概率法校正后,FCGR2A基因区域的rs1801274、BLK基因的rs2254546以及ABCC4基因的rs7329490、rs7986087、rs7320375各SNP位点基因型和等位基因频率在冠状动脉正常或增粗组、冠状动脉扩张组、冠状动脉瘤组中分布差异均无统计学意义(P均>0.05),见
川崎病可发生于世界各族人群,其中亚裔人群发病率高。即使在美国,亚裔婴幼儿的患病率较黑人高出3倍,而较白人高出6倍[6]。可见,遗传因素在川崎病的发生发展中扮演着重要的角色。川崎病遗传背景复杂,易感性可由多基因组成,目前国内外研究的川崎病易感基因主要分为两类:一类是参与炎性反应的基因,如基质金属蛋白酶基因、肿瘤坏死因子α基因、白细胞介素18基因等;另一类是参与血管功能的基因,如血管紧张素转化酶基因、血管源性生长基因等[7]。然而近年来,有学者通过全基因组关联分析对美国人群研究发现,FCGR2A、BLK、ABCC4等基因与川崎病遗传易感密切相关,随后有学者对日本、韩国、中国台湾、中国四川儿童等亚洲人群研究也得出较为一致的结果。本研究以华南地区儿童为对象,挑选出以往报道与川崎病易感最为相关的上述基因SNP位点进行研究。然而,研究中我们仅证实FCGR2A基因的rs1801274位点及BLK基因的rs2254546位点突变与川崎病易感相关。其中,FCGR2A基因rs1801274 (A/G)位点的OR<1,A为风险基因。BLK基因的rs2254546 (A>G)位点的OR>1,G为风险基因。
FCGR2A基因位于1号染色体FCGR基因群上,编码Fc gamma受体家族ⅡA(Fc gamma receptor Ⅱ A, FcγRIIA)蛋白,为IgG受体家族的成员,由2个共显性的等位基因A和G编码。等位基因A编码的受体在131氨基酸位点为组氨酸(H),而等位基因G编码的受体在131位点为精氨酸(R),因此个体可出现3种基因型:131H/H、131/R和131R/R[8,9]。研究表明,FCGR2A编码区的基因多态性可影响对IgG的亲和力。FCGR2A-H131基因编码的受体对IgG2和IgG3的亲和力较FCGR2A-R131编码的受体高,在FCGR2A的3种等位基因型中131H/H编码的受体亲合力最高,131R/R最低,131H/R居于两者之间[10]。因此,在不同个体中,即出现基于基因多态性产生的对IgG亚型敏感性强弱不同而导致的受体亲和力改变,从而影响感染性疾病和炎症的免疫应答。
在既往的8个病例对照研究中,来自中国台湾与四川、美国高加索地区、日本、韩国的2 973例川崎病患者与12 905名对照的资料被应用于FCGR2A rsl801274与川崎病易感的相关性分析,并发现FCGR2A受体基因的功能多态性位点在亚洲和其他种族之间A等位基因频率存在差异,其中编码组氨酸的风险等位基因A可提高川崎病的患病风险[11]。与本研究结果一致,川崎病组与正常对照组FCGR2A基因的SNP位点(rs1801274)基因型分布存在差异(χ2=98.17,P=0.000),且等位基因A频率在川崎病组(78.8%)显著高于正常对照组(30.9%),提示该位点A等位基因与川崎病的遗传易感密切相关。
编码酪氨酸激酶的BLK基因主要表达于B淋巴细胞。当B细胞表达的BLK上调时,可引起前B细胞增生并增强对IL的反应性,因此,BLK变化可影响B淋巴细胞免疫耐受的机制,使个体易产生自身免疫[12]。有研究分别以日本人、中国四川儿童为研究对象发现,BLK rs2254546(A/G)与川崎病显著相关,其中G等位基因型(GG)表现为高度易感性[2,13]。同样,本研究中,BLK基因的SNP位点rs2254546分布在正常对照组和川崎病组间差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.47,P=0.039),等位基因G频率在川崎病组(81.5%)高于正常对照组(74.0%),OR>1,进一步说明G等位基可能为川崎病遗传易感基因。
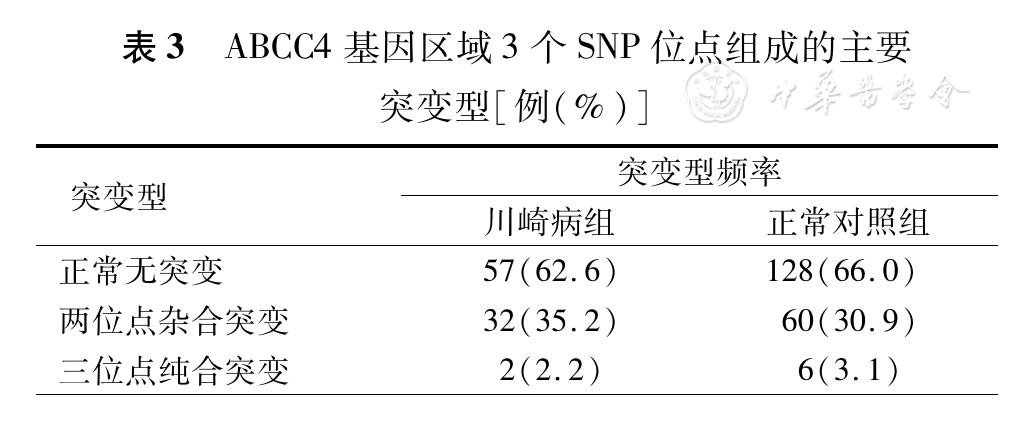
ABCC4基因又称多药耐药基因3(multidrug resistance 3,MDR3),位于人类染色体7q21.1,其编码的P糖蛋白属腺苷三磷酸(adenosine triphosphate, ATP)结合盒转运子家族,为多能循环单核苷酸转运体[14]。研究表明,ABCC4能向细胞外转运前列腺素2(prostaglandin 2, PEG2),并参与PEG2合成与分泌,因而能够促进炎症,可被非甾族抗炎药物抑制(阿司匹林)。川崎病是一种急性、自限性血管炎症性疾病,炎症贯穿了川崎病的始末,因此推测,该基因的SNP位点多态性在一定程度上可能影响川崎病的发生发展甚至川崎病的治疗。在以美国人群为对象的全基因组关联分析中发现,ABCC4 rs7986087、rs7329490与rs7320375与川崎病易感性呈正相关,且杂合子患川崎病的风险更高[4]。然而本研究结果并未能证实这一点,提示ABCC4基因区域的SNP位点多态性可能在遗传背景方面存在差异性。此外,对不同冠状动脉损伤的川崎病患儿分析中发现,ABCC4基因rs7320375位点等位基因频率在各组中分布差异亦无统计学意义(χ2=0.45, P=0.799; χ2=1.142, P=0.631)、(χ2=0.25,P=0.882; χ2=0.995, P=1.000)、(χ2=0.785, P=0.151; χ2=1.316, P=0.271)。究竟ABCC4基因与中国华南地区儿童川崎病易感的关联度如何仍有待进一步扩大样本量研究验证。
本研究验证了FCGR2A、BLK及ABCC4基因多态性与华南地区儿童川崎病遗传易感相关性,并发现FCGR2A基因rs1801274位点高风险的A等位基因,以及BLK基因rs2254546位点G等位基因分别对川崎病易感性有良好的提示作用,有望成为川崎病的辅助诊断指标。下一步有必要进一步扩大样本量,寻找川崎病及其并发症的高风险遗传因子,这对于川崎病早期发现并及时有效的干预具有重要意义。
[1] Chen KY,Curtis N,Dahdah N, et al. Kawasaki disease and cardiovascular risk: a comprehensive review of subclinical vascular changes in the longer term[J]. Acta Paediatr, 2016, 105(7): 752-761.
[2] Yan Y,Ma Y,Liu Y, et al. Combined analysis of genome-wide-linked susceptibility loci to Kawasaki disease in Han Chinese[J]. Hum Genet, 2013, 132(6): 669-680.
[3] Duan J,Lou J,Zhang Q, et al. A genetic variant rs1801274 in FCGR2A as a potential risk marker for Kawasaki disease: a case-control study and meta-analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e103329.
[4] Khor CC,Davila S,Shimizu C, et al. Genome-wide linkage and association mapping identify susceptibility alleles in ABCC4 for Kawasaki disease[J]. J Med Genet, 2011, 48(7): 467-472.
[5] Newburger JW,Takahashi M,Gerber MA, et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: a statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association[J]. Circulation, 2004, 110(17): 2747-2771.
[6] Rowley AH. Kawasaki disease: novel insights into etiology and genetic susceptibility[J]. Annu Rev Med, 2011, 62: 69-77.
[7] Kuo HC,Chang WC. Genetic polymorphisms in Kawasaki disease[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2011, 32(10): 1193-1198.
[8] Geva R,Vecchione L,Kalogeras KT, et al. FCGR polymorphisms and cetuximab efficacy in chemorefractory metastatic colorectal cancer: an international consortium study[J]. Gut, 2015, 64(6): 921-928.
[9] Kuo HC,Chang JC,Kuo HC, et al. Identification of an association between genomic hypomethylation of FCGR2A and susceptibility to Kawasaki disease and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance by DNA methylation array[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2015, 67(3): 828-836.
[10] Li R,Peng H,Chen GM, et al. Association of FCGR2A-R/H131 polymorphism with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus among Asian population: a meta-analysis of 20 studies[J]. Arch Dermatol Res, 2014, 306(9): 781-791.
[11] Khor CC,Davila S,Breunis WB, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies FCGR2A as a susceptibility locus for Kawasaki disease[J]. Nat Genet, 2011, 43(12): 1241-1246.
[12] Wu YY,Georg I,Díaz-Barreiro A, et al. Concordance of increased B1 cell subset and lupus phenotypes in mice and humans is dependent on BLK expression levels[J]. J Immunol, 2015, 194(12): 5692-5702.
[13] Onouchi Y,Ozaki K,Burns JC, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies three new risk loci for Kawasaki disease[J]. Nat Genet, 2012, 44(5): 517-521.
[14] Yu DM,Huynh T,Truong AM, et al. ABC transporters and neuroblastoma[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2015, 125: 139-170.
收藏此内容
推荐给朋友